The Eagle Bioscience’s Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Sensitive ELISA was utilized in two recent publications! On study explored how norepinephrine transporter defects lead to sympathetic hyperactivity in familial dysautonomia models and the other focused on the effects of a caffeine containing pre-workout supplement on β2-adrenergic and MAPK signaling during resistance exercise. Check out the full text and abstracts below.
Norepinephrine transporter defects lead to sympathetic hyperactivity in Familial Dysautonomia models
Abstract
Familial dysautonomia (FD), a rare neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorder affects the sympathetic and sensory nervous system. Although almost all patients harbor a mutation in ELP1, it remains unresolved exactly how function of sympathetic neurons (symNs) is affected; knowledge critical for understanding debilitating disease hallmarks, including cardiovascular instability or dysautonomic crises, that result from dysregulated sympathetic activity. Here, we employ the human pluripotent stem cell (hPSC) system to understand symN disease mechanisms and test candidate drugs. FD symNs are intrinsically hyperactive in vitro, in cardiomyocyte co-cultures, and in animal models. We report reduced norepinephrine transporter expression, decreased intracellular norepinephrine (NE), decreased NE re-uptake, and excessive extracellular NE in FD symNs. SymN hyperactivity is not a direct ELP1 mutation result, but may connect to NET via RAB proteins. We found that candidate drugs lowered hyperactivity independent of ELP1 modulation. Our findings may have implications for other symN disorders and may allow future drug testing and discovery.
Wu, HF., Yu, W., Saito-Diaz, K. et al. Norepinephrine transporter defects lead to sympathetic hyperactivity in Familial Dysautonomia models. Nat Commun 13, 7032 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-34811-7
The effects of a caffeine containing pre-workout supplement on β2-adrenergic and MAPK signaling during resistance exercise
Abstract
Aim: The acute myocellular responses of caffeine supplementation during resistance exercise (RE) have not been investigated. β2-Adrenergic receptors (β2AR) may be a target of the stimulatory effects of caffeine and stimulate bioenergetic pathways including protein kinase A (PKA), and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK).
Purpose: Elucidate the effects of pre-workout supplementation on signaling responses to an acute RE bout.
Methods: In a randomized, counter-balanced, double-blind, placebo-controlled, within-subject crossover study, ten resistance-trained males (mean ± SD; age = 22 ± 2.4 years, height = 175 ± 7 cm, body mass = 84.1 ± 11.8 kg) consumed a caffeine containing multi-ingredient pre-workout supplement (SUPP) or color and flavor matched placebo (PL) 60 min prior to an acute RE bout of barbell back squats. Pre- and post-exercise muscle biopsies were analyzed for the phosphorylation (p-) of β2AR, PKA, and MAPK (ERK, JNK, p38). Epinephrine was determined prior to supplementation (baseline; BL), after supplementation but prior to RE (PRE), and immediately after RE (POST).
Results: Epinephrine increased at PRE in SUPP (mean ± SE: 323 ± 34 vs 457 ± 68 pmol/l; p = 0.028), and was greatest at POST in the SUPP condition compared to PL (5140 ± 852 vs 2862 ± 498 pmol/l; p = 0.006). p-β2AR and p-MAPK increased post-exercise (p < 0.05) with no differences between conditions (p > 0.05). Pearson correlations indicated there was a relationship between epinephrine and p-β2AR in PL (r = − 0.810; p = 0.008), and p-β2AR and ERK in SUPP (r = 0.941; p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Consumption of a caffeine containing pre-workout supplement improves performance, possibly through increases in pre-exercise catecholamines. However, the acute myocellular signaling responses were largely similar post-exercise.
Nicoll, J.X., Fry, A.C. & Mosier, E.M. The effects of a caffeine containing pre-workout supplement on β2-adrenergic and MAPK signaling during resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 123, 585–599 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-022-05085-0
If you have any questions about our Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Sensitive ELISA or our other offerings, please contact us here.
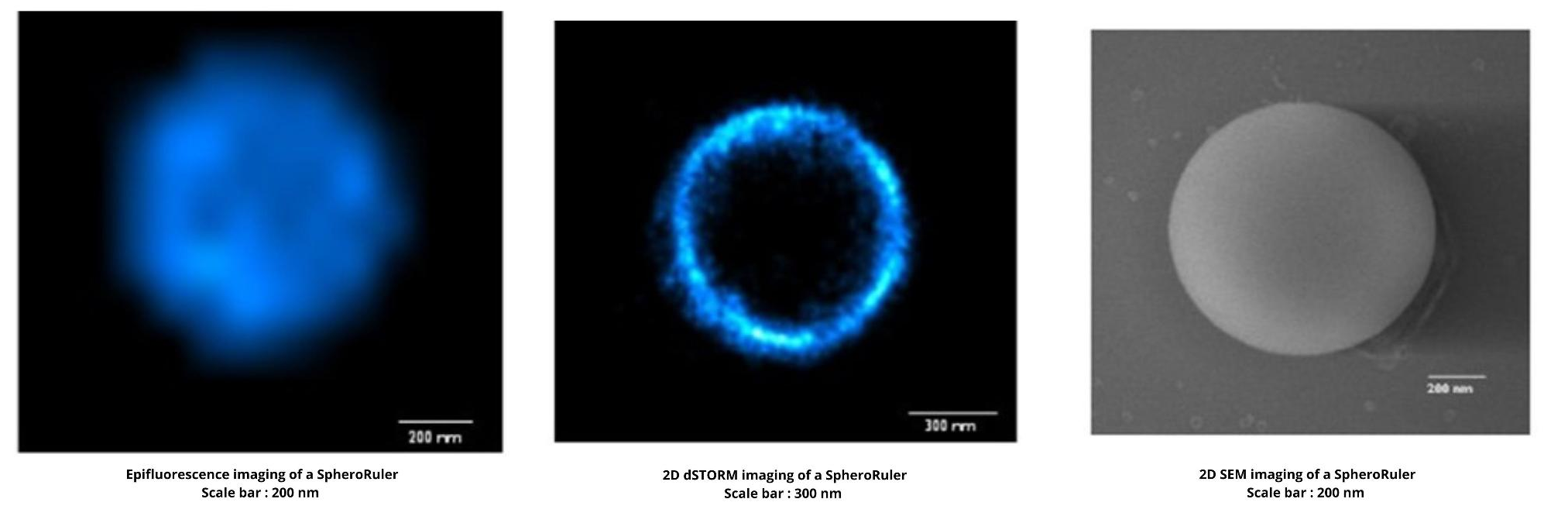
 What is it SpheroRuler intended for?
What is it SpheroRuler intended for?