
Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF-23) is a hormone primarily produced by osteocytes and osteoblasts in bones, playing a key role in regulating phosphate and vitamin D metabolism. It lowers serum phosphate levels by reducing phosphate reabsorption in the kidneys and suppresses the activation of vitamin D, thereby decreasing intestinal phosphate and calcium absorption. FGF-23 requires the co-receptor Klotho to bind to fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs) and exert its effects, primarily in the kidneys. Dysregulation of FGF-23 is associated with several pathological conditions, making it a valuable biomarker for assessing phosphate balance and mineral metabolism.
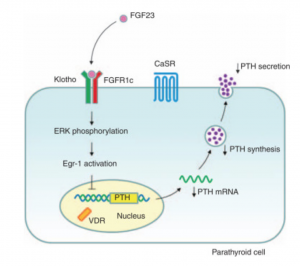
image credit: https://www.kidney-international.org/
Why Measure FGF-23?
Measuring FGF-23 is essential for advancing research on phosphate metabolism, bone biology, and endocrine regulation. It provides insights into the mechanisms underlying phosphate homeostasis and the complex interplay between FGF-23, Klotho, and fibroblast growth factor receptors. FGF-23 is also a valuable marker for studying how mineral metabolism affects systemic processes, including cardiovascular function and aging. In experimental models, FGF-23 measurements help elucidate the effects of genetic mutations, dietary phosphate intake, and novel therapeutic interventions on phosphate regulation. Additionally, FGF-23 serves as a biomarker to explore the broader effects of mineral dysregulation on inflammation, oxidative stress, and metabolic disorders, enhancing our understanding of its role in health and disease.
Related Products:
- FGF23 Intact ELISA Assay Kit*
- FGF23 C-Terminal ELISA Assay Kit*
- MedFrontier Intact FGF23 CLEIA Assay Kit
*Use Promo Code: FGF25 to save 25% on your order!

