What
are Natriuretic peptides?
The natriuretic peptides belong to a family of
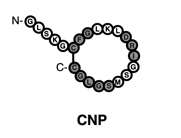
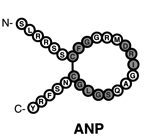
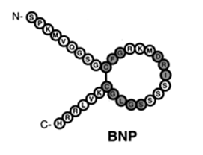
structurally similar but genetically different peptide hormones and include atrial, brain, and C type (ANP, BNP, and CNP, respectively). A-type and B-type have primarily have functions in the cardiovascular system and make up the cardiac natriuretic peptides. The discovery of this family was a major breakthrough in modern medicine and more specifically, cardiovascular physiology. This finding provided a direct connection between the heart and the kidneys with respect to the regulation of natriuresis.
These natriuretic peptides are modulated through their cognate receptors which are known as the ANP-A (a.k.a. NPR-A, GC-A), ANP-B (a.k.a. NPR-B, GC-B) and ANP-C (a.k.a NPR-C) receptors. ANP and BNP
preferentially bind to a membrane bound guanylyl cyclase (GC) receptor called
GC-A or NPR1, whereas CNP is the physiological ligand for GC-B (NPR2).
All natriuretic peptides are produced as propeptides,
which are then cleaved into the biologically active, C-terminal hormone
and the N-terminal fragment (NT-proANP 1-98, NT-proBNP 1-76 and NT-proCNP). It has been discovered that N-terminal fragments are
much more stable, and circulate in higher amounts than the active hormones. Thus, for these reasons the N-terminal fragments are easier and more reliable for measurement in serum or plasma.
The natriuretic peptides play an important role in the
regulation of cardiovascular and renal homeostasis and in the regulation of
fatty acid metabolism and body weight. In addition, in recent
studies natriuretic peptides have been proven to be valuable biomarkers for cardiac
pathology, including myocardial ischaemia and left ventricular dysfunction, as
well as risk stratification in congestive heart failure (CVD).
Natriuretic peptides have a wide range of roles and
effects on several biological functions within the body as seen below.
Biological Functions of Natriuretic
peptides:
- Natriuresis
- Vasodilation
- Homeostasis
- Inhibition of
aldosterone system - Inhibition of
renin-angiotensin system - Inhibition of
vascular smooth muscle growth (i.e. myocardial, endothelial, smooth
muscle) - Inhibition of
ADH hormone - Inhibition of
aldosterone hormone
References
- Clerico A et al. “Thirty years of the heart as an endocrine organ: physiological role and clinical utility of cardiac natriuretic hormones.” Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011; 301: H12-H20.
- Doust, Jenny et al. “The Role of BNP Testing in Heart Failure.” American Family Phyisician; 2006 Dec 1;74(11):1893-190.
- Lauridsen, Bo K et al. “ProANP Plasma Measurement Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Acutely Hospitalized Patients: A Cohort Study.” BMJ Open 2013;3:e003288 doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003288
- Moro, Cedric et al. “Natriuretic Peptides: New Players in Energy Homeostasis.” Diabetes 2009; 12: 2726-2728
- Nazario, B et al. “Atrial and Brain Natriuretic Peptides Stimulate the Production and Secretion of C-type Natriuretic Peptide from Bovine Aortic Endothelial Cells.” Journal of Clinical Investigation 1995 Mar; 95(3): 1151–1157.
- Schreibe, Donald et al. “Natriuretic Peptides in Congestive Heart Failure.” Medscape 2012: Jan 10.
- Suzuki, T et al. “The Role of the Natriuretic Peptides in the Cardiovascular System.” Cardiovascular Research 2001; 51: 489–494.
- Stanek, B. et al. “Prognostic evaluation of neurohumoral plasma levels before and during beta-blocker therapy in advanced left ventricular dysfunction” Journal of American Cardiology 2001; 38: 436-442
Related Resources Citing EagleBio Kits:
- Stanek, B. et al. “Prognostic evaluation of neurohumoral plasma levels before and during beta-blocker therapy in advanced left ventricular dysfunction” Journal of American Cardiology 2001; 38: 436-442.
Related Kits:
proANP ELISA Assay Kit
BNP Fragment (Nt-proBNP 8-29) ELISA Assay Kit
NT-proCNP ELISA Assay Kit
Cardiovascular Assay Kits
Related News:
EagleBio Spotlight: ANP
EagleBio Spotlight: BNP
EagleBio Spotlight: CNP
Interesting Study Highlighting Eagle Biosciences’ BNP Fragment ELISA Assay Kit