Human IL-6 High Sensitivity ELISA Assay
The Human IL-6 High Sensitivity ELISA Assay is Developed and Manufactured in Austria by Biomedica
Size: 12×8 wells
Sensitivity: 0.28 pg/ml
Dynamic Range: 0 – 200 pg/ml
Incubation Time: 4 hours 30 minutes
Sample Type: Serum, Plasma, Cell Culture Supernatants, Urine
Sample Size: 100 µl
Alternative Name: Interleukin 6
Assay Principle
The Human IL-6 High Sensitivity ELISA Assay Kit is a sandwich enzyme immunoassay that has been optimized and fully validated for the quantitative determination of human IL-6 in serum, EDTA-plasma, citrate plasma, and heparin plasma. Validation experiments have been performed according to international quality guidelines (ICH/ FDA/ EMEA). Cell culture supernatant and urine samples are compatible with this ELISA. The IL-6 ELISA assay recognizes both natural and recombinant human IL-6. The assay employs highly purified epitope mapped antibodies as well as human serum-based standards and controls. The figure below explains the principle of the human IL-6 sandwich ELISA:
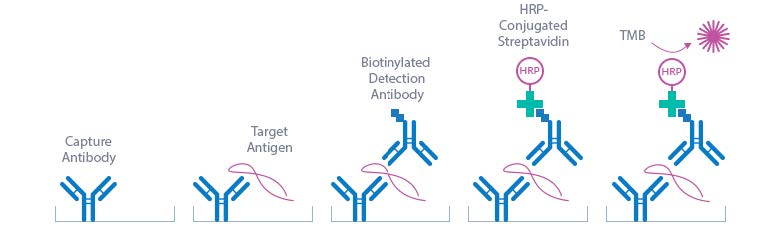
In a first step, STD/sample/CTRL are pipetted into the wells, which are pre-coated with the recombinant anti-human IL-6 antibody. Any soluble IL-6 present in the STD/sample/CTRL binds to the pre-coated anti-IL-6 antibody in the well. After incubation, a washing step is applied where all non-specific unbound material is removed. In a next step, the biotinylated anti-IL-6 antibody (AB) is pipetted into the wells and reacts with the IL-6 present in the sample, forming a sandwich. Next, all unbound antibody is removed during another washing step. In the next step, the con-jugate (streptavidin-HRPO) is added and reacts with the biotinylated anti-IL-6 antibody. After another washing step, the substrate (tetramethylbenzidine; TMB) is pipetted into the wells. The enzyme catalysed color change of the substrate is directly proportional to the amount of IL-6 present in the sample. This color change is detectable with a standard microtiter plate ELISA reader. A dose response curve of the absorbance (optical density, OD at 450 nm) versus standard concentration is generated, using the values obtained from the standards. The concentration of soluble IL-6 in the sample is determined directly from the dose response curve.
Related Products
Human CD126 IL-6R ELISA Assay
Human IL-2 HS ELISA Assay
Human High Sensitive IFN-gamma ELISA Assay
Assay Background
IL-6 PROTEIN
Interleukin-6 (IL-6), also known as B-cell stimulatory factor 2 (BSF-2), CTL differentiation factor (CDF), Hybridoma growth factor or Interferon beta-2 (IFN-beta-2), was success-fully cloned by Hirano et al. in 1986. The gene is mapped at chromosome 7p21. IL-6 protein is built up by 183 amino acids and has a calculated molecular weight of 20.8 kDa. It is a pleiotropic, alpha helical protein that is composed of a four-helix bundle. It shares 39% sequence identity with mouse and 40% with rat IL-6. IL-6 is phosphorylated at amino acid 81 and it is variably glycosylated by N-linked glycosylation. IL-6 belongs to the IL-6/GCSF/MGF protein family whose members share a common use of the gp130 receptor subunit. IL-6 isoforms, with internal deletions, are generated by alternative splicing. The principal cell sources for IL-6 are mononuclear phagocytes, vascular endothelial cells, fibroblasts or other cells. IL-6 is the ligand for the Interleukin-6 receptor α (IL-6Rα) that occurs membrane-bound, but that may also circulate as soluble form generated by alternative splicing or proteolytic cleavage. To induce signaling, IL-6 first forms a complex with the non-signaling IL-6Rα. Subsequent binding to the signal transducing subunit gp130 leads to dimerization of gp130 and finally to the formation of the hexameric signaling complex. Complexes of IL-6 and soluble IL-6Rα may elicit responses in cells lacking the membrane-bound IL-6Rα but expressing the ubiquitous gp130 coreceptor. This process is known as trans-signaling, it enlarges the spectrum of target cells responding to IL-6.
IL-6 FUNCTION
IL-6 is immediately produced in response to infections or tissue injury, and it plays a major role in host defense. After synthesis the principal cellular targets of IL-6 are liver cells where IL-6 leads to the synthesis of acute phase proteins, B cells where proliferation of antibody producing cells is induced, or T cells where differentiation is induced. Signaling is induced by homodimerization of the receptor complex upon IL-6 binding, and subsequent activation of Janus kinases that then phosphorylate tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of gp130. Two main pathways are activated in the signaling event: the MAPK and the JAK/STAT pathway. IL-6 expression is tightly regulated, and mis-regulation contributes to chronic inflammation and autoimmunity. IL-6 plays an important role in acute phase reaction, inflam-mation, hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression. Increased IL-6 levels were observed in inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, castleman’s disease, or sepsis. In this context, pro-inflammatory activities seem to depend mainly on IL-6 trans-signaling via sIL-6Rα. IL-6 also has anti-inflammatory activities that depend on membrane-bound IL-6Rα. In healthy individuals, IL-6 levels in the blood are reported in the single-digit pg/ml range. However, during inflammatory states IL-6 levels can increase several thousand-fold. Targeting of the IL-6 pathway has led to innovative therapeutic approaches for various rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, adult-onset Still‘s disease, giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis, as well as other conditions such as Castleman disease and cytokine release syndrome. Targeting this pathway has also identified avenues for potential expansion into several other indications, such as uveitis, neuromyelitis optica and, most recently, COVID-19 pneumonia.
Areas of Interest
- Inflammation
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis
- Castleman´s disease
- Sepsis
- Cancer
- Bone metabolism
- Cardiovascular disease
- Metabolic syndrome
- Covid-19
Typical Standard Curve

Package Inserts
Please note: All documents above are for reference use only and should not be used in place of the documents included with this physical product. If digital copies are needed, please contact us.