Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit
The Blood Urea Nitrogen Detection Kit is For Research Use Only
Size: 2×96 wells
Sensitivity: 0.030 mg/dl
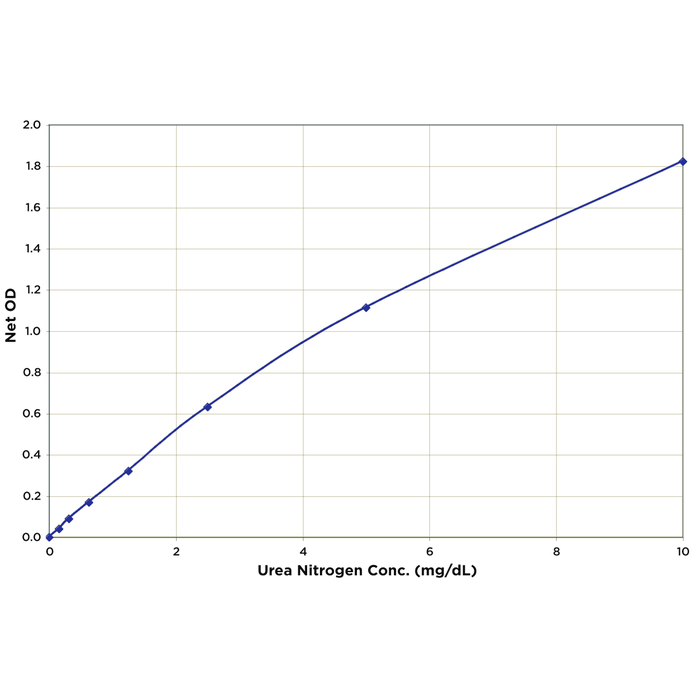
Dynamic Range: 0.156 – 10 mg/dl
Incubation Time: 30 minutes
Sample Type: Plasma, Saliva, Serum, Tissue Culture Media, Urine
Sample Size: 50 μL
Product manufactured in Canada by StressMarq.
Assay Principle
A urea nitrogen standard calibrated to NIST reference materials is provided to generate a standard curve for the assay and all samples should be read off the standard curve. Samples are mixed with Color Reagents A and B and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes. The colored product is read at 450 nm. The concentration of urea nitrogen in the sample is calculated, after making a suitable correction for any dilution, using software available with most plate readers. The results are expressed in terms of mg/dL urea nitrogen. If samples are to be expressed in terms of mg/dL urea, the data can be converted using the multiplier 2.14.
Typical Standard Curve