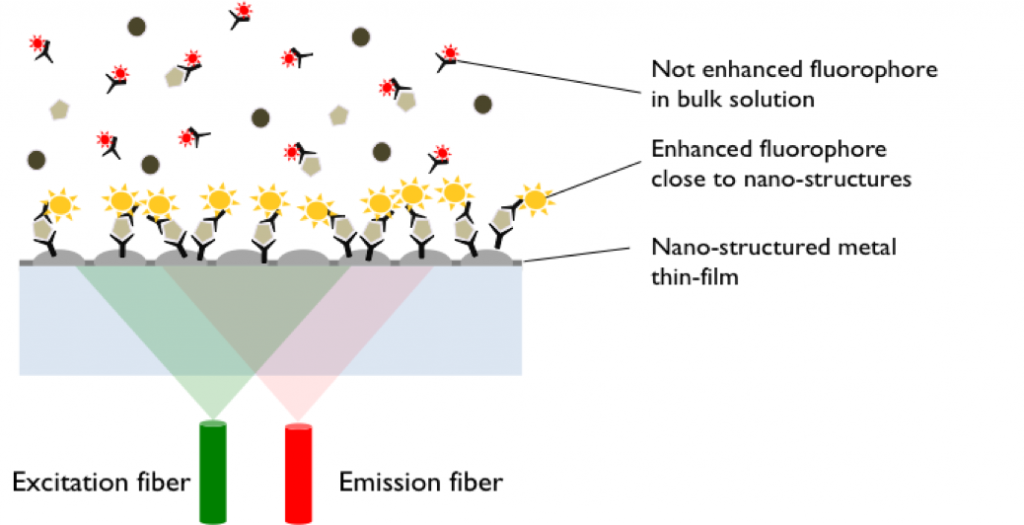
Eagle Biosciences partner Fianostics completed a study evaluating their Noggin and Asporin FluoBolt assays as biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The study shows that NOGGIN and ASPORIN may be valuable biomarkers for the diagnosis of NAFLD patients and they may also mediate the favorable effect of vitamin E treatment, although mechanistic studies are needed. Further studies with higher patient numbers are also required to confirm these promising results. The study helps support that these highly sensitivity assays allow researchers to measure a decrease of both markers in samples from NAFLD patients. This measurement is not possible with less sensitive methods. This indicates that noggin and asporin may be valuable biomarkers for NAFLD diagnosis.
Contact us for more information about these kits or our other FluoBolt offering.