Swine IL-4 ELISA Assay
The Swine IL-4 ELISA Assay is For Research Use Only
Size: 1×96 wells
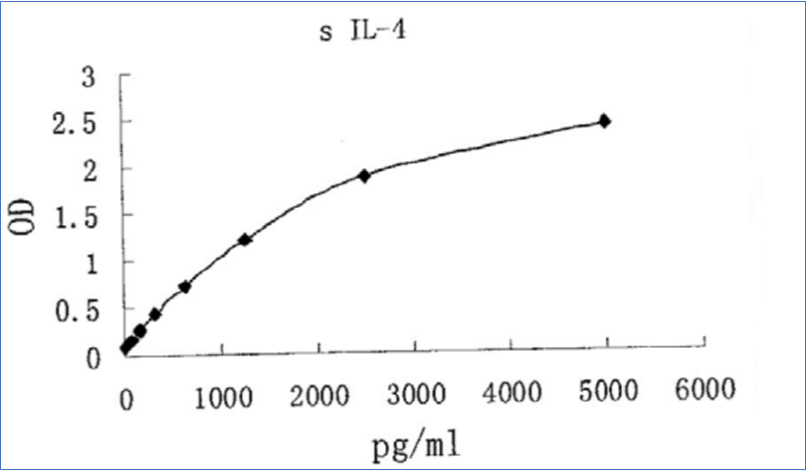
Sensitivity: 7 pg/mL
Dynamic Range: 15.625 – 500 pg/ml
Incubation Time: 3.5 hours
Sample Type: Serum, Plasma, Cell Culture
Sample Size: 100 µl
Alternative Names: Porcine Interleukin 4, Porcine IL-4, Swine Interleukin 4, B cell Stimulatory Factor 1
Assay Background
Interleukin 4 (IL-4), also known as B cell stimulatory factor 1, is a monomeric, approximately 13-18 kDa Th2 cytokine that shows pleiotropic effects during immune responses.It is a glycosylated polypeptide that contains three intrachain disulfide bridges and adopts a bundled four αhelix structure. Porcine IL-4 is synthesized with a 24 amino acid (aa) signal sequence. Mature porcine IL-4 shares 78%, 59%, 41%, and 41% aa sequence identity with bovine, human, mouse, and rat IL-4, respectively. Human IL-4 is active on porcine vascular endothelial cells. IL-4 exerts its effects through two receptor complexes. The type I receptor, which is expressed on hematopoietic cells, is a heterodimer of the ligand binding IL-4 Rα and the common γ chain (a shared subunit of the receptors for IL-4, -7, -9, -15, and -21). The type II receptor on nonhematopoietic cells consists of IL-4Rα and IL13Rα1. The type II receptor also transduces IL-13 mediated signals. IL-4 is primarily expressed by Th2-biased CD4+ T cells, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. It promotes cell proliferation, survival, and immunoglobulin class switch to IgE in B cells, acquisition of the Th2 phenotype by naïve CD4+ T cells, priming and chemotaxis of mast cells, eosinophils, and basophils, and the proliferation and activation of epithelial cells. IL-4 plays a dominant role in the development of allergic inflammation and asthma.
Related Products
Swine IL-2 ELISA Assay
Swine IL-10 ELISA Assay Kit
Human IL-4 ELISA Assay