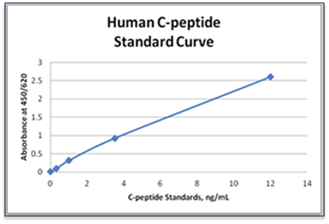
C-Peptide ELISA Kit
C-peptide is a 31-amino acid peptide released as a byproduct during the enzymatic cleavage of proinsulin into insulin within pancreatic beta cells. As proinsulin is split, insulin and C-peptide are secreted into the bloodstream in equimolar concentrations. Notably, C-peptide has a longer half-life than insulin—approximately three to four times longer—which makes it a more stable and reliable biomarker for assessing endogenous insulin production.
Clinically, C-peptide measurement is a valuable tool in evaluating beta cell function, particularly in distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. In type 2 diabetes, C-peptide levels may be normal or elevated, indicating sufficient insulin production but resistance at the receptor level. Conversely, low or absent C-peptide in insulin-treated individuals suggests diminished or absent endogenous insulin secretion, a characteristic of type 1 diabetes. C-peptide testing is also useful in diagnosing causes of hypoglycemia and in monitoring residual beta cell activity in diabetic patients undergoing insulin therapy.
Beyond diabetes, emerging research indicates that C-peptide may play a role in inflammatory pathways and vascular complications. Studies have suggested that C-peptide can exert chemotactic effects on immune cells and may contribute to the development of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes, further highlighting its relevance as both a diagnostic and potential prognostic biomarker in metabolic and cardiovascular disease.
This C-Peptide ELISA Kit is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.