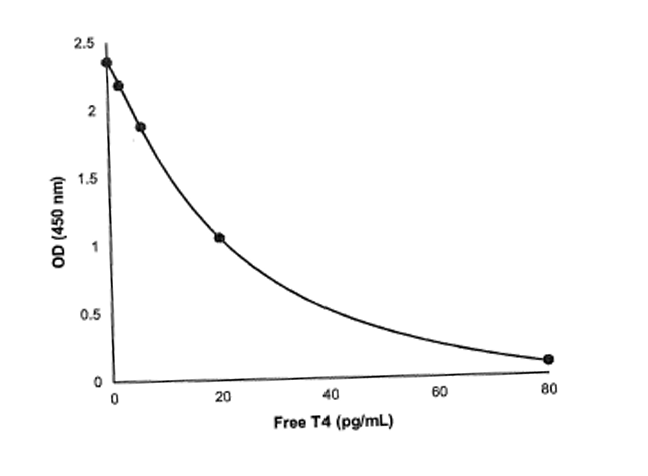
Free thyroxine (free T4) is the unbound, biologically active form of thyroxine, one of the primary hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Most circulating T4 is bound to transport proteins like thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG), rendering it inactive; only a small fraction exists as free T4, which is capable of entering cells and being converted to the more active hormone triiodothyronine (T3). Free T4 plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development by influencing numerous physiological processes through gene expression.
In clinical and research settings, free T4 is a fundamental biomarker for assessing thyroid function and diagnosing thyroid disorders such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Measuring free T4 provides a more accurate reflection of thyroid hormone status than total T4, especially in conditions where binding protein levels are altered, such as pregnancy, liver disease, or the use of certain medications. Clinically, free T4 is used alongside thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to evaluate thyroid health, guide treatment decisions, and monitor the effectiveness of thyroid hormone replacement therapy. In research, it serves to explore the regulation of thyroid function and its impact on systemic health, including cardiovascular, metabolic, and cognitive outcomes.
This product is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.