Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody (IgG1) that targets tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), a key pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in a variety of chronic inflammatory diseases. By binding with high affinity to both the soluble and transmembrane forms of TNFα, infliximab prevents it from interacting with its receptors, thereby interrupting the downstream inflammatory signaling cascade. This includes the inhibition of cytokines like IL-1, IL-6, and the suppression of endothelial adhesion molecules and matrix-degrading enzymes. As a result, infliximab reduces inflammation, cell migration, and tissue damage in affected areas.
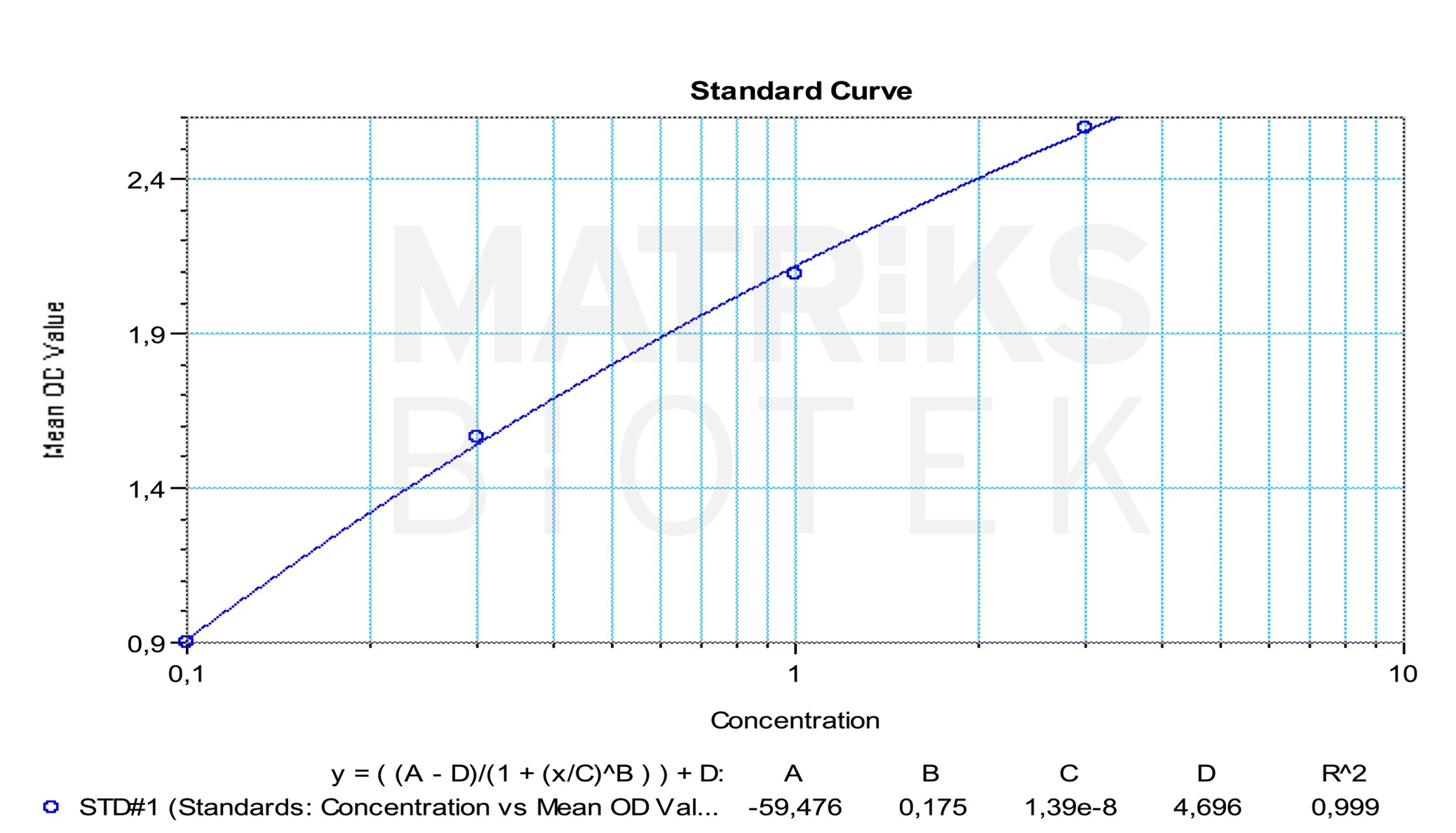
In clinical practice, infliximab is used in the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, and ankylosing spondylitis. It plays a crucial role in therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), where maintaining optimal serum concentrations is essential for therapeutic efficacy while avoiding toxicity. TDM can also assist in identifying poor compliance and immunogenicity-related issues, especially in patients who may develop antidrug antibodies (ADAs) that reduce the drug’s effectiveness.
In research settings, infliximab is used as a model TNFα inhibitor to study inflammatory disease mechanisms, evaluate cytokine suppression, and assess ADA development. Given its chimeric composition—75% human and 25% murine—it is also frequently studied in immunogenicity research to better understand how structural differences influence ADA formation and clinical outcomes. These insights are critical for developing next-generation biologics with reduced immunogenic potential.
This product is manufactured in Turkey by Matriks Biotek.