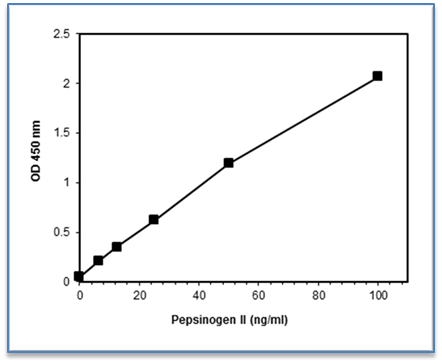
Pepsinogen II ELISA Kit
Pepsinogen II (PGII) is a zymogen, or inactive precursor, of the digestive enzyme pepsin and is primarily produced by gastric chief cells located in the fundus, antrum, and proximal duodenum. Unlike Pepsinogen I (PGI), which is secreted mostly in the fundic glands, PGII has a wider expression pattern within the gastrointestinal tract, making it particularly informative for assessing gastric function and pathology. In acidic conditions within the stomach, PGII is converted into its active form, pepsin, aiding in protein digestion.
In clinical diagnostics, serum PGII levels are valuable for evaluating gastric mucosal health. Elevated PGII is commonly associated with Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric conditions such as chronic gastritis, peptic ulcers, and certain types of gastric cancer. The ratio of PGI to PGII is a widely recognized non-invasive biomarker for diagnosing gastric atrophy and estimating the risk of developing gastric carcinoma. This ratio is especially useful in population-based gastric cancer screening programs, notably in East Asia, where the disease burden is higher. PGII testing complements other biomarkers such as gastrin-17 in comprehensive gastric function panels.
In research applications, PGII serves as a critical marker in studies focused on gastrointestinal disease progression, therapeutic efficacy, and the impact of H. pylori eradication on gastric cancer risk reduction. It is also being explored in contexts like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Advanced immunoassay platforms, including ELISA and chemiluminescent assays, have improved the accuracy and efficiency of PGII quantification, broadening its utility in both clinical diagnostics and research protocols for early disease detection and monitoring.
This Pepsinogen II ELISA Kit is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.