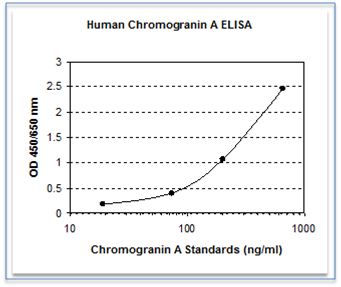
Chromogranin A ELISA Kit
Chromogranin A (CgA) is a glycoprotein secreted by neuroendocrine cells and neurons, serving as a precursor to several bioactive peptides such as catestatin, pancreastatin, and vasostatins. These peptides are involved in regulating various physiological processes, including blood pressure, metabolism, and immune responses. Chromogranin A is present in most neuroendocrine cells and is co-secreted with other hormones upon cell stimulation. Its measurement in blood has been utilized as a biomarker for neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), particularly those originating from the gastrointestinal tract and pancreas.
In clinical practice, Chromogranin A is commonly used to aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of NETs. Elevated levels of CgA are often observed in patients with gastroenteropancreatic NETs (GEP-NETs), and its concentration correlates with tumor burden and disease progression. However, the sensitivity and specificity of Chromogranin A as a diagnostic tool can vary depending on the type and location of the tumor, as well as the assay methods used. Despite its utility, Chromogranin A is not without limitations; factors such as proton pump inhibitor use can falsely elevate CgA levels, and its sensitivity may be lower in poorly differentiated tumors. Moreover, CgA’s role as a prognostic marker is still under investigation, with some studies suggesting its potential in assessing treatment response and predicting disease recurrence. Overall, while Chromogranin A remains a valuable tool in the management of NETs, it is often used in conjunction with other biomarkers and imaging modalities to provide a comprehensive assessment of the disease.
This Chromogranin A ELISA Kit is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.