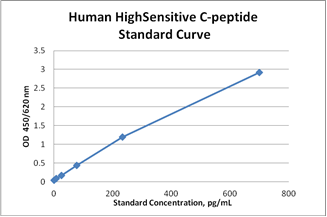
C-Peptide Ultrasensitive ELISA Kit
Human ultra sensitive C-peptide is a refined biomarker used to detect extremely low levels of C-peptide in the bloodstream, enabling more precise assessment of endogenous insulin production. C-peptide, a 31-amino acid peptide, is cleaved from proinsulin during the formation of insulin in the pancreatic beta cells and circulates in equimolar amounts with insulin. Due to its longer half-life—approximately three to four times that of insulin—C-peptide serves as a more stable and reliable marker of beta-cell function.
In clinical practice, ultra sensitive C-peptide assays are especially valuable for evaluating residual beta-cell activity in patients with long-standing diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes where C-peptide levels may be extremely low. These measurements aid in distinguishing between type 1 and type 2 diabetes, investigating causes of hypoglycemia, and monitoring disease progression or therapeutic interventions. In individuals with insulin resistance (type 2 diabetes), preserved or elevated C-peptide levels indicate adequate insulin production with poor cellular response.
Research suggests that beyond glucose metabolism, C-peptide may exert biological effects such as influencing inflammatory pathways. Studies have implicated C-peptide in the chemotaxis of immune cells and a potential role in promoting atherosclerotic changes, especially in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Ultra sensitive assays thus offer a powerful tool for both clinical diagnostics and metabolic or cardiovascular research.
This C-Peptide Ultrasensitive ELISA Kit is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.