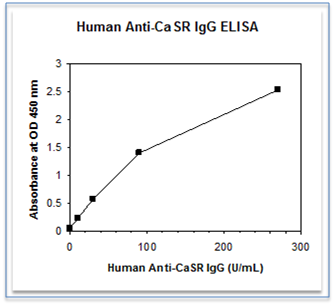
Anti-CaSR IgG ELISA Kit
The calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a G protein-coupled receptor composed of 1,078 amino acids, primarily located in the parathyroid glands and kidneys. It plays a critical role in maintaining calcium homeostasis by regulating parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion and renal calcium reabsorption in response to extracellular calcium levels. Genetic mutations in the CaSR gene, located on chromosome 3q21.1, have been linked to disorders such as familial benign hypocalciuric hypercalcemia (FBHH/FHH) and neonatal severe primary hyperparathyroidism (NSHPT).
Anti-CaSR IgG autoantibodies have emerged as a significant biomarker in diagnosing autoimmune forms of hypoparathyroidism. These autoantibodies have been detected in patients with FHH who lack CaSR gene mutations, as well as in those with acquired autoimmune hypoparathyroidism—either as an isolated condition or as part of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndromes (APS-1 and APS-2). These syndromes often involve combinations of endocrine and autoimmune conditions such as Addison’s disease, autoimmune thyroiditis, type 1 diabetes, and mucocutaneous candidiasis.
In both clinical and research settings, the detection of anti-CaSR IgG is valuable for determining the autoimmune etiology of hypoparathyroidism. Its presence supports early and accurate diagnosis, which is essential for guiding immunosuppressive treatment strategies and monitoring disease progression or recurrence, especially in patients without identifiable genetic mutations.
This Anti-CaSR IgG ELISA Kit is manufactured in USA by Eagle Biosciences.