

What
is BNP?
BNP stands for Brain natriuretic peptide or otherwise
known as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and is produced from a preprohormone
precursor. BNP was named after it was originally identified in extracts of
porcine brain, hence brain natriuretic peptide.
Even though in humans, this peptide is produced mainly in the cardiac
ventricles its name remains the same. Following cardiac hemodynamic stress,
both atrial natriutetic peptide (ANP) and BNP are secreted from the heart (primarily produced by atrial and
ventricular cardiomyocytes). BNP is mainly expressed by ventricular myocardium
in response to volume overload and increased filling pressure. BNP
may be only activated after a prolonged period of volume overload and thus
acting like a backup hormone in response to heart stress.
The release of BNP into the blood stream causes
dilation of the blood vessels, and thereby dilation of the arteries. This begins the process of the body’s natural
response to reduce blood pressure in the body, followed by blockage of adrenalin,
and finally the release of sodium and water into the urine (natriuresis). Healthy individuals typically exhibit the
highest BNP concentrations in the atria but BNP is shifted to the ventricles in
heart failure (HF). A high concentration of BNP in the bloodstream is
indicative of heart failure. In fact, BNP
is predictive of cardiac dysfunction, in particular left ventricular
dysfunction, and is a useful marker of future outcomes in patients with acute
coronary syndromes and congestive heart failure.
Biochemical structure of BNP:
BNP is produced as a 108 amino acid precursor protein
which is cleaved into a biologically active 32 amino acid carboxyl-terminal
fragment and a 76 amino acid amino- terminal fragment.
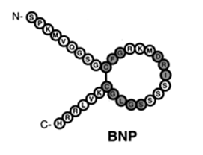
Conserved residues are shaded and the line
within the ring represents the disulfide bond.
The N-terminal peptide comprising amino acids 1-76 is further degraded proteolytically and thus BNP fragments in the circulation are very heterogeneous. There are a few different circulating forms of BNP such as BNP-32 (77-108), a high molecular weight BNP and and the NT-proBNP (1-76).
The BNP fragment (Nt-proBNP 8-29) is the preferred analyte for representation of BNP status for a few reasons. BNP Fragment is a stable molecule, has a long half-life and it circulates in high concentrations.
Why Measure BNP?
BNP has a key role in cardiovascular homeostasis with biological actions including natriuresis, diuresis, vasorelaxation, and inhibition of renin and aldosterone secretion. Because of its broad range of functions in the body, measuring this analyte can be used for studying and/or monitoring the diseases/conditions below.
Diseases/conditions associated with elevated BNP levels:
- Diabetes and
Obesity - Renal Disease/Renal
dysfunction - Hypertension
- Pneumonia
- Asthma
attacks - Recent
heart attack - Heart
failure/Cardiac impairment - Cardiomyopathy
- Sepsis
- Sleep
apnea
References
- Clerico A et al. “Thirty years of the heart as an endocrine organ: physiological role and clinical utility of cardiac natriuretic hormones.” Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2011; 301: H12-H20.
- Davis, William et al. “A Special Test to Diagnose Heart Failure.” Life Extension Magazine; 2007: Jun.
- Doust, Jenny et al. “The Role of BNP Testing in Heart Failure.” American Family Phyisician; 2006 Dec 1;74(11):1893-190.
- Mair, Johannes. “What are the differences between NT-proBNP and BNP, and do they matter?” Cardiac Biomarkers; 2011: Dec 1;74(11):1893-1900.
- Moro, Cedric et al. “Natriuretic Peptides: New Players in Energy Homeostasis.” Diabetes 2009; 12: 2726-2728.
- Suzuki, T et al. “The Role of the Natriuretic Peptides in the Cardiovascular System.” Cardiovascular Research 2001; 51: 489–494
Related Resources Citing EagleBio Kits:
Related Kits:
BNP Fragment (Nt-proBNP 8-29) ELISA Assay Kit
Related News:
EagleBio Spotlight: Natriuretic Peptides
Interesting Study Highlighting Eagle Biosciences’ BNP Fragment ELISA Assay Kit

