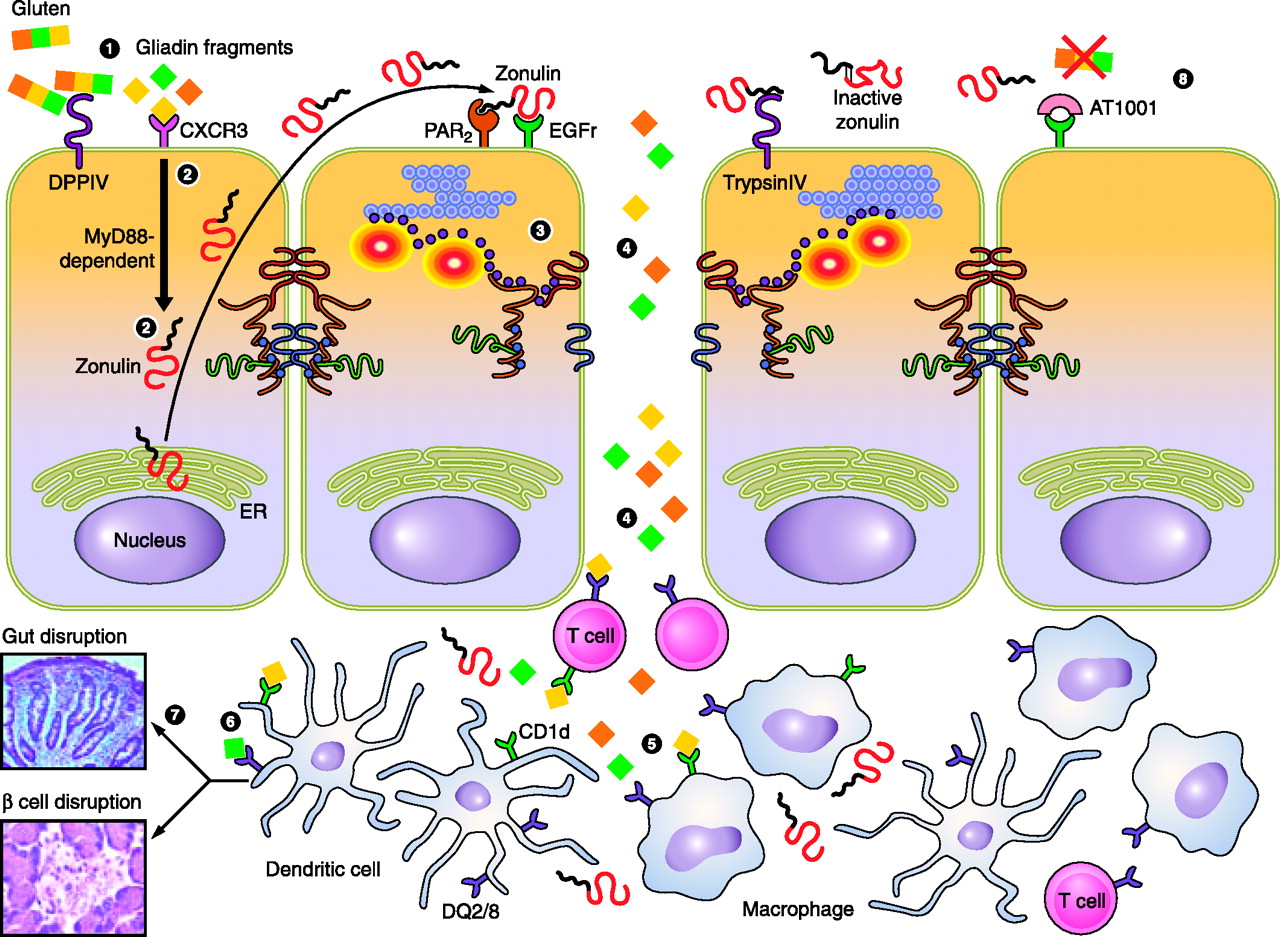
The zonulin biomarker is a pre-haptoglobin (pre-HP2) protein found in the gut. It is responsible for the permeability of the mucosal barrier of the intestines. When zonulin binds to the epithelial cells of the intestines a signal cascade is induced. This cascade disassembles the paracellular tight junctions of the intestinal wall. The tight junctions of the intestinal walls are one of two ways that allow molecules to transfer from the gut lumen to the bloodstream and vice versa.
Why Measure Zonulin?
When zonulin levels in the gut increase and go out of balance, these junctions open wider and stay open longer. These widened entry points allow larger macromolecules into the bloodstream or into the gut lumen. The molecules that pass through these breaches can increase the body’s natural immune reaction, causing inflammation and a number of autoimmune diseases.
Diseases Associated with Increased Zonulin Levels:
- Celiac Disease
- Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
- Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS-D)
- Type-1 Diabetes
- Liver Disease
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
image credit: https://physrev.physiology.org/
Related Kits